FastVLM Ablations
Code implementation of Apple's FastVLM with video fine-tuning and inference capabilities

This repository contains our comprehensive research implementation and extensions of FastVLM: Efficient Vision Encoding for Vision Language Models (CVPR 2025) by Apple Inc. FastVLM introduces FastViTHD, a hybrid vision encoder that revolutionizes efficiency by outputting ~100 tokens per image compared to 576 for traditional CLIP-based models.
Project Overview
Our study encompasses two major components:
- Video Fine-tuning Adaptation - Extended FastVLM for video-text pair training
- Windows Inference Engine - Built real-time inference system with live webcam support
1. Video Fine-tuning Adaptation
We successfully extended FastVLM to support video-text pair training using a sparse temporal sampling strategy, enabling the model to understand temporal sequences while maintaining efficiency.
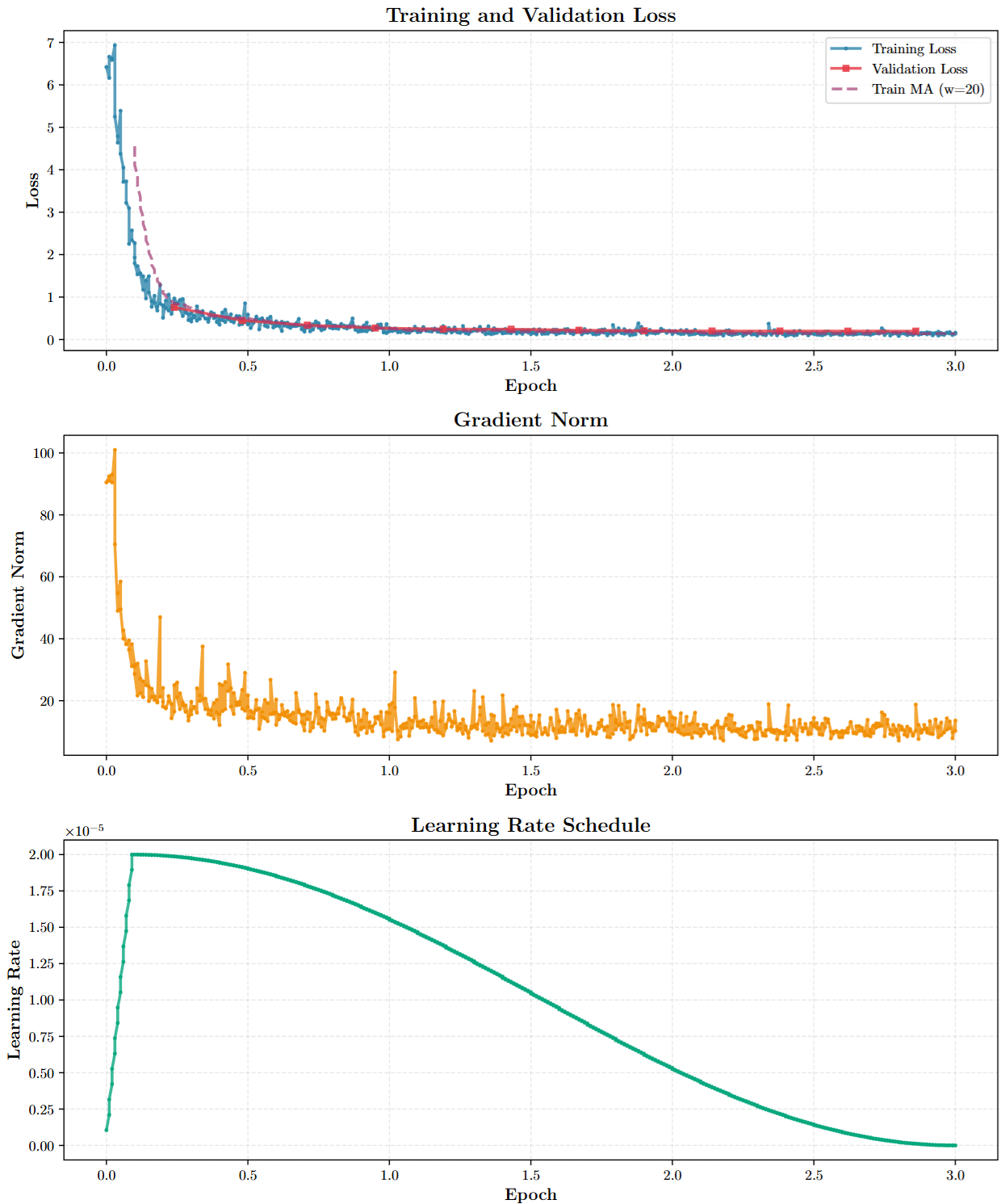
Key Innovation: Frames as Images Approach
Our adaptation treats videos as sequences of uniformly sampled frames, where each frame is processed independently through the vision encoder before concatenation. This "flipbook" approach enables:
- Simplicity: No architectural changes required to the vision encoder or language model
- Compatibility: Existing image-trained models can be directly fine-tuned on videos
- Efficiency: ~800 tokens for 8 video frames vs 4,608 for CLIP-based models
Technical Implementation
- Video Loading Functions: Added utility functions to detect and process video files
- Dataset Modifications: Extended
LazySupervisedDatasetto handle both images and videos - Token Expansion Strategy: Modified
preprocess_multimodal()to expand<image>tokens - Configuration Parameters: Added video-specific training arguments
Training Configuration:
- Sparse temporal sampling (4-8 frames per video)
- Batch processing with mixed precision training
- Validation on video-text datasets
- Monitored metrics: loss convergence, BLEU scores, temporal coherence
Note: Fine-tuning implementation is available at EdgeVLM-Labs/fastvlm-adaptation as it requires modifications to core training code in the llava/ module.
Results & Performance
- Training Stability: Consistent loss convergence across video datasets
- Temporal Understanding: Successfully learned to process sequential visual information
- Backward Compatibility: Maintained performance on image-only task
2. Windows Inference Engine
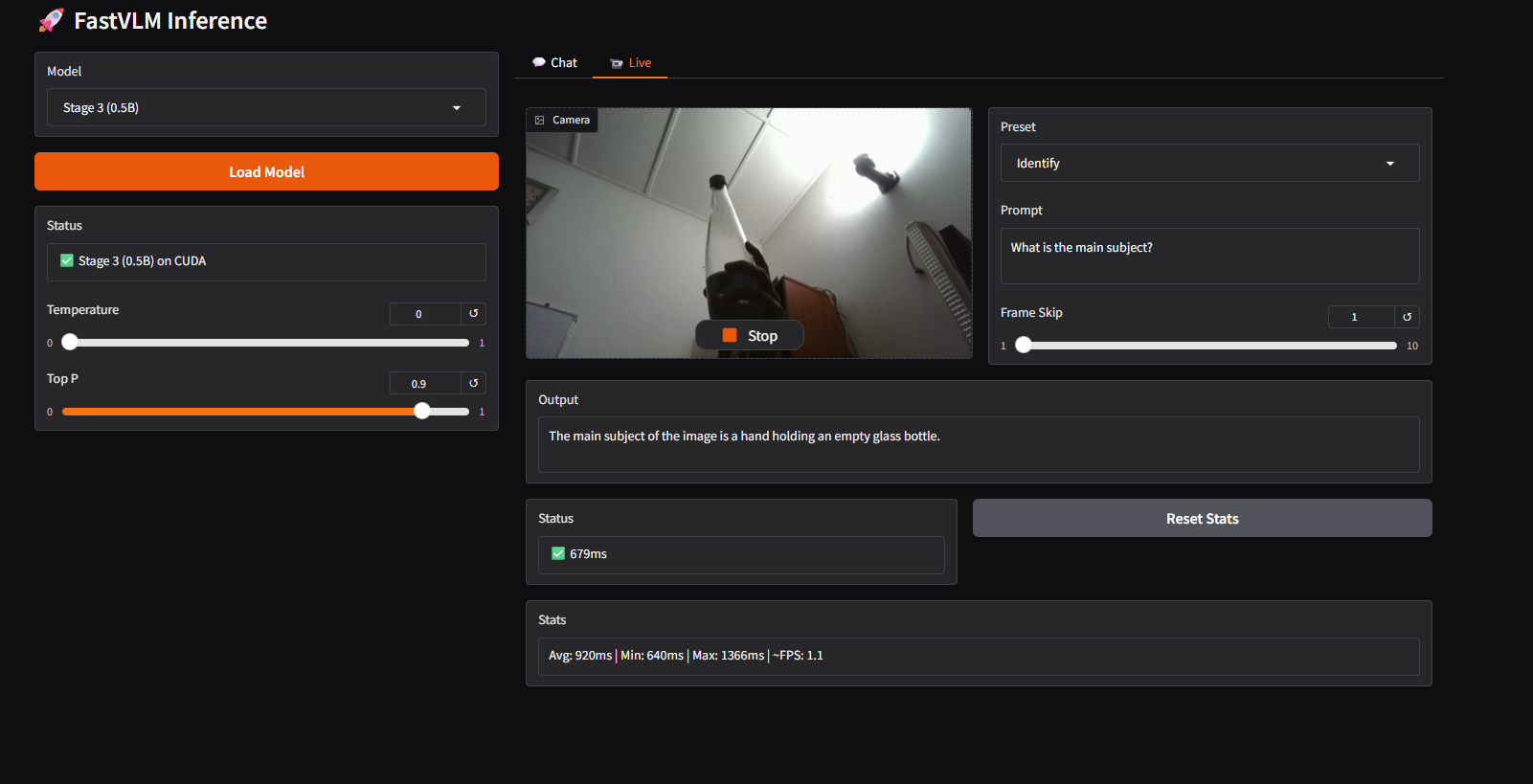
Developed a production-ready Gradio-based inference application featuring dual modes for both static image analysis and real-time webcam streaming with performance optimizations.
Core Features
1. Dual Operation Modes
The system supports two primary modes of interaction. In Chat Mode, users can upload images for detailed analysis using either custom or preset prompts such as describing scenes, counting objects, etc. This mode provides full-length, detailed responses along with performance metrics like TTFT and TPS.
In Live Mode, the system operates on real-time webcam streams, performing continuous frame capture and inference with adjustable frame skipping (1-10x) to balance performance and responsiveness. Responses are optimized for brevity to ensure smooth streaming, while live performance statistics are displayed in real time.
2. Performance Optimizations
- Prompt Caching
- Frame Skipping
- GPU Acceleration
- Response Optimization
Tokenized prompts are cached to avoid repeated tokenization, significantly reducing overhead for recurring queries, with automatic cache invalidation whenever the prompt changes.
An adjustable frame skip rate (1–10 frames) is used during live streaming to reduce computational load while maintaining a balance between responsiveness and visual coverage.
Inference is accelerated using TF32 on Ampere and newer GPUs, combined with FP16 precision and efficient memory cleanup to maximize performance and stability.
Model outputs are cleaned and optimized by removing redundant formatting, intelligently completing sentences, and limiting response length in live mode to ensure smooth real-time interaction.
System Requirements
- Python 3.10+
- CUDA-enabled GPU (recommended for real-time performance)
- 8GB+ VRAM for Stage 3 model
- Windows/Linux compatible
This project demonstrates the practical application of cutting-edge vision-language research, extending capabilities to temporal understanding while maintaining efficiency, and delivering a production-ready inference system for real-world deployment.
References
[1] P. K. A. Vasu, F. Faghri, C.-L. Li, C. Koc, N. True, A. Antony, G. Santhanam, J. Gabriel, P. Grasch, O. Tuzel, and H. Pouransari, "FastVLM: Efficient Vision Encoding for Vision Language Models," in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2412.13303
Contributors
For detailed documentation, setup instructions, and code examples, visit the GitHub repository.